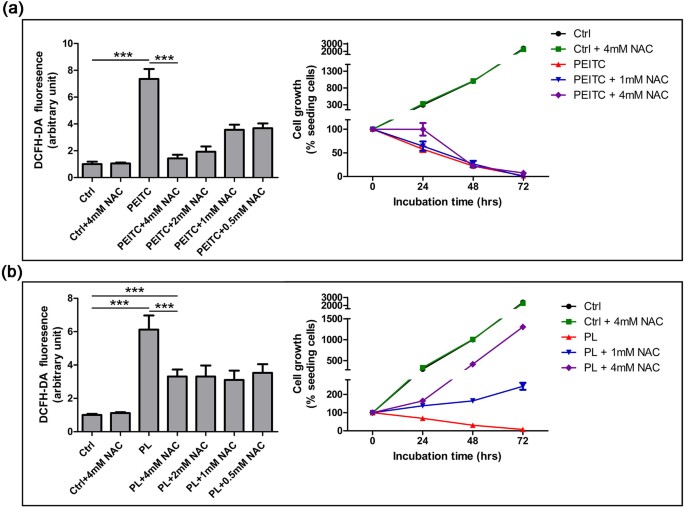
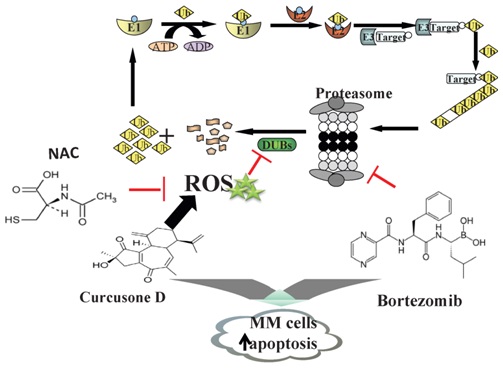
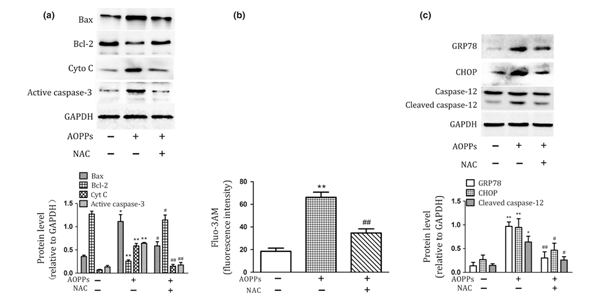
![N-acetylcysteine alleviates PCB52-induced hepatotoxicity by repressing oxidative stress and inflammatory responses [PeerJ] N-acetylcysteine alleviates PCB52-induced hepatotoxicity by repressing oxidative stress and inflammatory responses [PeerJ]](https://dfzljdn9uc3pi.cloudfront.net/2020/9720/1/fig-5-full.png)
N-acetylcysteine alleviates PCB52-induced hepatotoxicity by repressing oxidative stress and inflammatory responses [PeerJ]
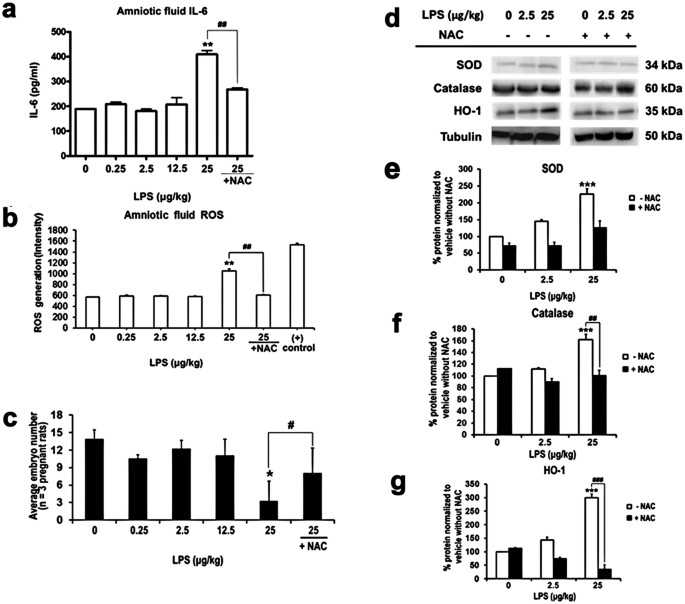
N-acetylcysteine attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced impairment in lamination of Ctip2-and Tbr1- expressing cortical neurons in the developing rat fetal brain | Scientific Reports

Effects of N-acetyl cysteine on mitochondrial ROS, mitochondrial dynamics, and inflammation on lipopolysaccharide-treated human apical papilla cells | SpringerLink

ROS inhibitor NAC compromises cytotoxicity of ADM/DAC treatment in HCC-LM3 and SMMC-7721 cell lines but does not impact glucose metabolism which is depressed by DAC.

N-Acetylcysteine amide, a Thiol Antioxidant and Neuroprotective Agent, Reduces ROS Production - Immune System Research

Regulation of Reactive Oxygen Species by Atm Is Essential for Proper Response to DNA Double-Strand Breaks in Lymphocytes | The Journal of Immunology
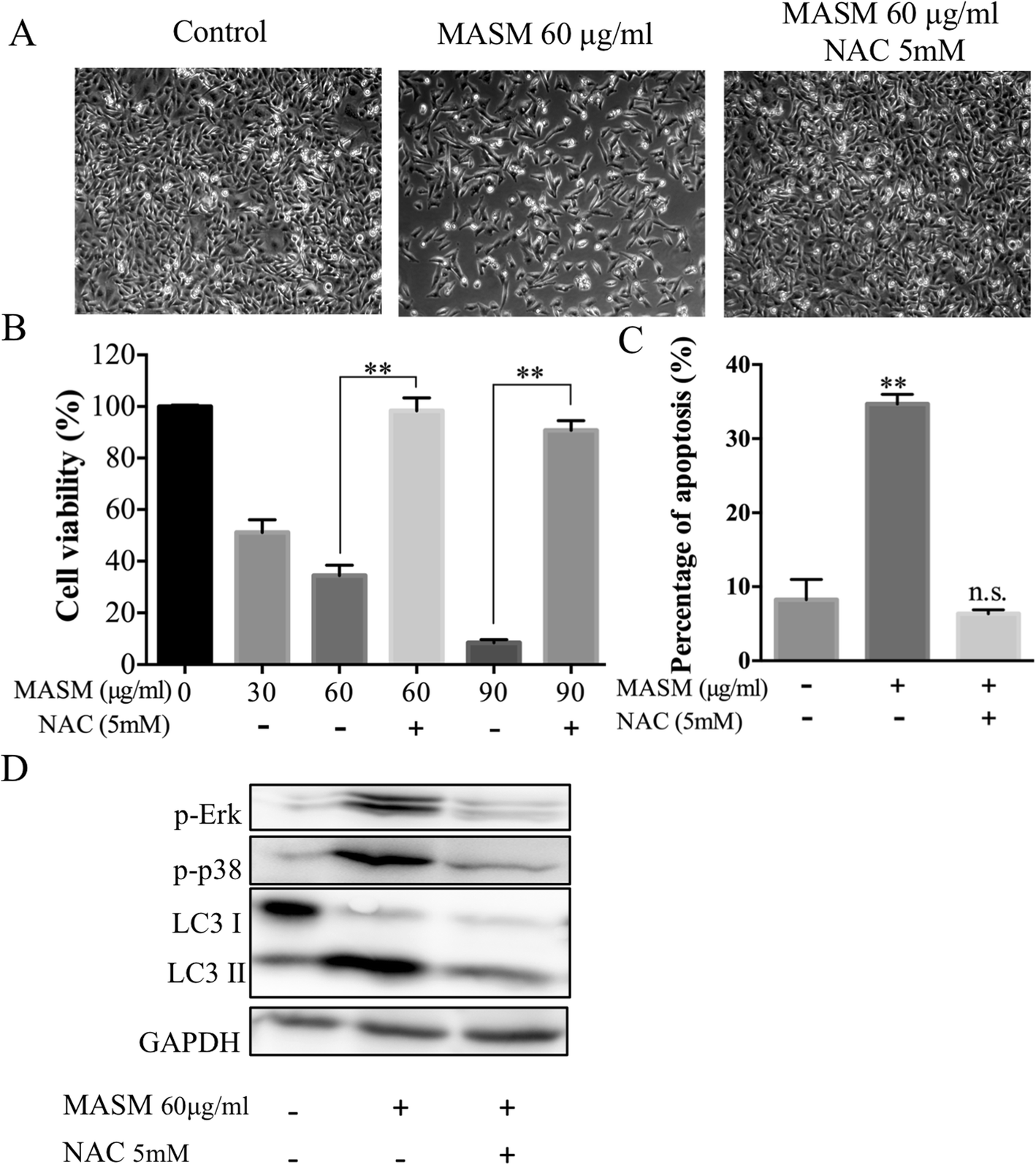
Autophagy inhibition enhances Matrine derivative MASM induced apoptosis in cancer cells via a mechanism involving reactive oxygen species-mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR and Erk/p38 signaling | BMC Cancer | Full Text

Importance of ROS-mediated autophagy in determining apoptotic cell death induced by physapubescin B - ScienceDirect

Effect of the reactive oxygen species (ROS) inhibitor N-acetylcysteine... | Download Scientific Diagram

ROS scavenger, N‐acetyl‐l‐cysteine and NOX specific inhibitor, VAS2870 reduce platelets apoptosis while enhancing their viability during storage - Hosseini - 2019 - Transfusion - Wiley Online Library

Figure 5 from Effect of N-acetyl-L-cysteine on ROS production and cell death caused by HEMA in human primary gingival fibroblasts. | Semantic Scholar

The mechanism of action of N-acetylcysteine (NAC): The emerging role of H2S and sulfane sulfur species - ScienceDirect

Attenuation of MG132-induced HeLa Cell Death by N-Acetyl Cysteine via Reducing Reactive Oxygen Species and Preventing Glutathione Depletion | Anticancer Research
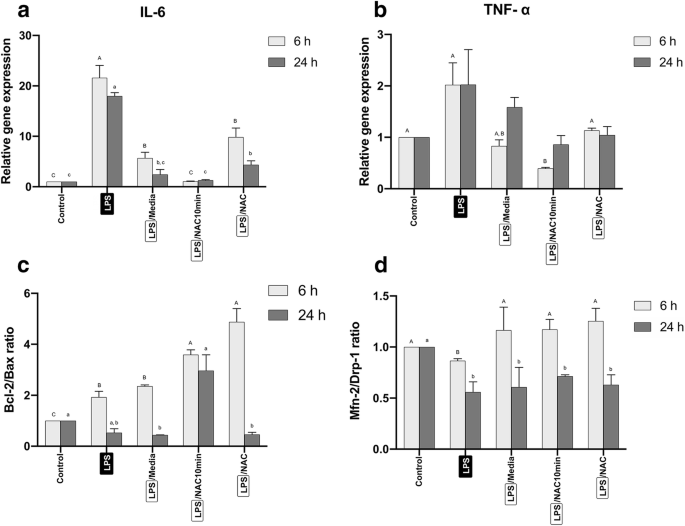
Effects of N-acetyl cysteine on mitochondrial ROS, mitochondrial dynamics, and inflammation on lipopolysaccharide-treated human apical papilla cells | SpringerLink
N-Acetyl Cysteine Depletes Reactive Oxygen Species and Prevents Dental Monomer-Induced Intrinsic Mitochondrial Apoptosis In Vitro in Human Dental Pulp Cells | PLOS ONE

N-Acetylcysteine Reduces ROS-Mediated Oxidative DNA Damage and PI3K/Akt Pathway Activation Induced by Helicobacter pylori Infection